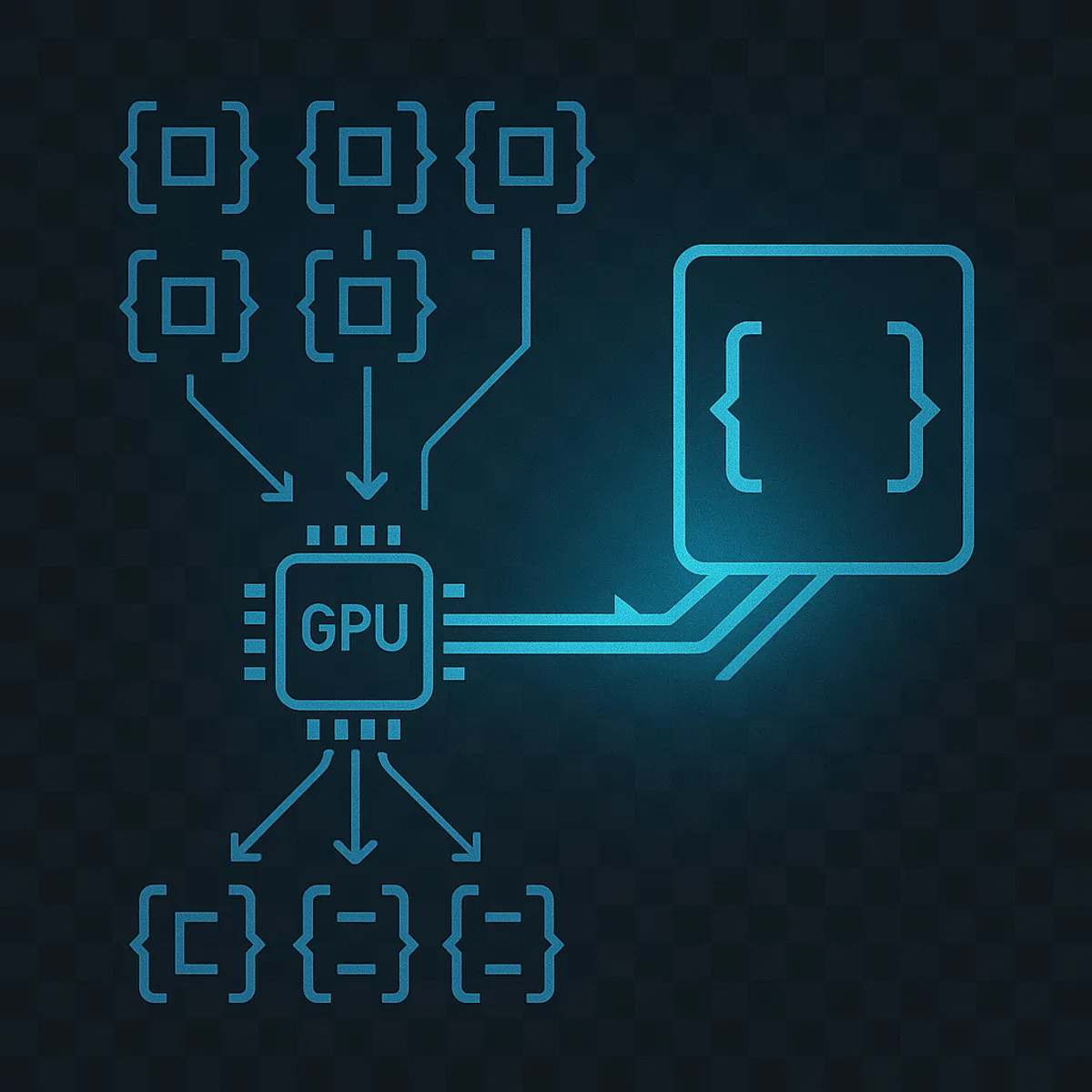
When submitting small tasks to the GPU, grid scheduling and synchronization costs may be much higher than computations, even on a CPU. In this case, the benefit of GPU computing is lost. Leveraging runtime compilation, we illustrate an approach that generates source code to replace a list of library API calls into a single kernel call.
The benefits are twofold:
- Scheduling costs are reduced to a minimum, as several calls are merged into a single one.
- Executing an aggregate kernel on a vector of values results in a compute-bound implementation.
Resources:
- Poster PDF: gtc-2017-poster